Hair loss in alopecia areata, occurs when hair follicles—naturally limited in number and cycling through growth, rest, and shedding phases—are affected by genetics, aging, autoimmune conditions, stress, or medical treatments, leading to temporary or permanent thinning and requiring preventive or restorative treatments.
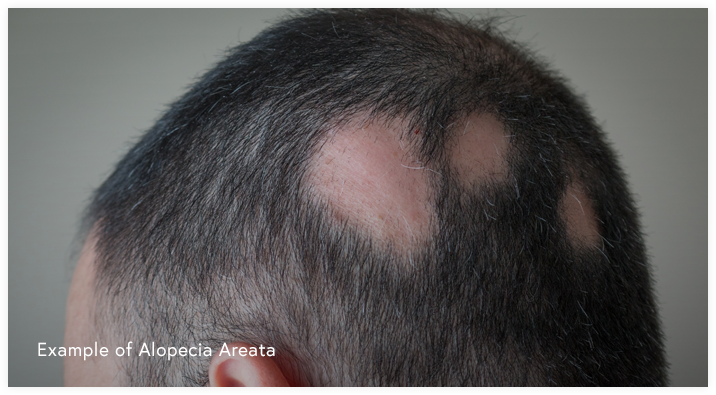
Alopecia Areata is the medical term for hair loss. There are many types of hair loss caused by a variety of conditions from autoimmune diseases to the use of certain medications.
Temporary hair loss can result from giving birth or from severe stress. Hair loss may be reversible or reverse on its own. Permanent hair loss is commonly caused by androgenetic alopecia areata or hereditary hair loss affects men and women. Everyone loses 50 – 100 scalp hairs each day. Usually, those hairs grow back.
Hair follicles are created before birth and remain constant throughout life. There are about 100,000 – 150,000 scalp hair follicles at birth. But not all follicles become active at the same time, and some lose the ability to produce hair over time.
Active follicles have a normal life cycle that includes a growth phase, followed by a transitional phase, and then a resting phase. In fact, hair grows one centimeter a month! And, not all hair follicles are active at the same time. The life cycle of hair follicles can be as long as seven years or as short as two years. The cycle ends when the hair is shed.

Contrary to popular belief, hereditary hair loss is not from the mother or mother’s father. Rather, multiple genes have been identified as causing male pattern hair loss and female pattern hair loss.
Get in touch with us and we’ll reply to your inquiry within a few hours.
Copyright© 2025 Hudson Dermatology & Laser Surgery